Diagnosis of Follicular Thyroid Cancer
- The diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer cannot be made by fine needle aspiration of a thyroid nodule!
- The diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer in a thyroid nodule can only be obtained by complete removal of the thyroid mass
- The diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer accounts for less than 10% of all thyroid cancers
- The diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer is three times more common in women than in men
- The diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer occurs most commonly above 40 years of age and rarely occurs in children
- Follicular thyroid cancer rarely spreads to lymph nodes (far less than 10%)
- The diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer is rarely associated with a history of radiation exposure
Diagnosis of Follicular Thyroid Cancer: How Is It Made?
Fine needle aspiration of a thyroid mass cannot diagnosis follicular thyroid cancer because it can only provide analysis of the cells themselves (which have the same appearance of normal follicular cells of the thyroid). The diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer within a thyroid gland can only be made by complete removal of the thyroid mass and then microscopic examination of the mass within the thyroid. The microscopic detection of these cells of the thyroid called follicular cells invading (or growing into) blood vessels, lymphatic vessels or the capsule of the thyroid mass are required for the diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer. If you have a needle biopsy that suggests a follicular neoplasm, then identifying an expert in thyroid cancer surgery is the most important next step! You must have surgery to diagnosis a follicular thyroid cancer. Thus finding an expert thyroid cancer surgeon is the first and most important step. It is not just your surgeon, however, it is your whole thyroid cancer surgery team. From the evaluation through to the surgery and post operative care, the whole surgical team is inovled in your care. See what our patients say about their surgeons and thyroid cancer team on our Google reviews. Here are some of our reviews and 5 star ratings on Google.
Follicular thyroid cancer patients rarely present with symptoms, but when symptoms do exist, the most common symptom is a lump in the neck. Other symptoms which may occur with the diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer may include changes in the quality of their voice, difficulty swallowing or breathing, and pain or tenderness in or around the neck or ear. Any diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer associated with change in voice, swallowing, difficulty breathing or pain are very serious symptoms and require prompt and thorough evaluation.
Diagnosis of Follicular Thyroid Cancer: other diagnoses that cannot be distinguished by fine needle aspiration analysis (this is called a differential diagnosis)
- Follicular adenoma ( this is not cancer!)
- Follicular neoplasm of uncertain malignant potential (this is not cancer!)
- Adenomatoid hyperplasia (this is not cancer!)
- Follicular variant of papillary thyroid cancer (this is a type of papillary thyroid cancer)
- Microinvasive (or minimally invasive) follicular thyroid cancer (this is a favorable type of follicular thyroid cancer that is cured by a thyroidectomy)
- Angioinvasive follicular thyroid cancer (this is a follicular thyroid cancer cured by total thyroidectomy)
- Widely invasive follicular thyroid cancer (this is the bad follicular thyroid cancer!)
- Complete Medical History and Physical Examination
- Surgical excision of the thyroid nodule with complete microscopic analysis (fine needle aspiration cannot diagnosis follicular thyroid cancer unless it is fna of a metastasis)
- Scans and Xrays
- Ultrasound
- CT Scan
- MRI Scan
- PET/CT Scan
- Blood Tests
- TSH
- T3 and T4
- Thyroglobulin (we obtain but not all doctors do so)
- Thyroglobulin Antibody (we obtain because it lets us know if there is an underlying inflammatory condition of the thyroid)
- Laryngoscopy (looking at the voice box)
Medical history and physical examination is required for all patients with a potential diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer. If there is a suspicion that you may have a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer, your health care professional will want to know your complete medical history. You will be asked questions about your possible risk factors, symptoms, and any other health problems or concerns. If someone in your family has had a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer, this is an important factor. Your doctor will examine you to get more information about possible signs of thyroid cancer and other health problems. During the exam, the doctor will pay special attention to the size and firmness of your thyroid and any enlarged lymph nodes in your neck. Examination of your voice box is part of the physical examination obtained by the surgeon for any thyroid lump. This is called a laryngoscopy and more is written about it at the end of this section.
If there has been a FNA and a follicular neoplasm has been suggested, a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer is possible therefore your health care professional will want to know your complete medical history. You will be asked questions about your possible risk factors, symptoms, and any other health problems or concerns.
Your doctor will examine you to get more information about possible signs of thyroid cancer and other health problems. During the exam, the doctor will pay special attention to the size and firmness of your thyroid and any enlarged lymph nodes in your neck. Examination of your voice box is part of the physical examination obtained by the surgeon for any thyroid lump. This is called a laryngoscopy and utilizes a small lighted instrument with a camera on the end to visualize the voice box . It is a simple examination obtained without the need for sedation or discomfort to examine the vocal cords and their function.
The Diagnosis of Follicular Thyroid Cancer is Made by Thyroidectomy
- The diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer cannot be made with an ultrasound guided small sampling of cells from the thyroid gland (The process of obtaining this small sampling of cells is called fine needle aspiration (FNA) cytology)
- The diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer within the thyroid requires thyroid surgery (lobectomy or total thyroidectomy)
- In rare circumstances, abnormal lymph nodes will be seen in follicular thyroid cancer and FNA of those lymph nodes will exhibit "follicular cells".
- The diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer is highly suggested when distant spread of disease is suggested in lung, bone, or liver and a follicular neoplasm of the thyroid is present.
- The first step leading to a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer requires obtaining a small sampling of cells with a skinny needle. This is called fine needle aspiration (FNA) cytology
- This type of biopsy can usually be done in your doctor’s office or clinic.
- Before the biopsy, local anesthesia (numbing medicine) may be injected into the skin over the thyroid nodule.
- Your doctor will place a thin, hollow needle directly into the nodule to aspirate (take out) some cells and possibly a few drops of fluid into a syringe.
- The doctor usually repeats this 2 or 3 more times, taking samples from several areas of the nodule.
- The content of the needle and syringe are then placed on a glass slide and then the FNA samples are then sent to a lab, where they are looked at under a microscope by the expert Cytologist to see if the cells look cancerous or benign.
- Cytology means looking at just the cells under the microscope.
- Thyroid cytology requires an expert physician (called a Cytologist) trained specifically in the diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer!!!
- Unfortunately, the diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer is frequently misinterpreted by unskilled or inexperienced Cytologists.
- The thyroid cytologist can only diagnose a follicular neoplasm (see the potential different diagnoses that may be associated with this FNA result)
- Bleeding at the biopsy site is very rare except in people with bleeding disorders. Even when this occurs, the bleeding is almost always very self limited. Be sure to tell your doctor if you have problems with bleeding or are taking medicines that could affect bleeding, such as aspirin or blood thinners.
- Sometimes an FNA biopsy will need to be repeated because the samples didn’t contain enough cells.
- Most FNA biopsies will show that the thyroid nodule is benign.
- Rarely, the FNA biopsy may come back as benign even though a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer is actually present.
Concern Over A Diagnosis of Follicular Thyroid Cancer: What If The Diagnosis is Not Clear?
Most of the time, FNA results from a follicular thyroid cancer (carcinoma) will be interpreted as a "follicular neoplasm" or "follicular lesion". If this happens, some doctors may order tests on the sample to see if there are genetic abnormalities noted (changed). There are several commercially available tests that doctors can send the samples to determine the risk of the cells being cancerous. Before you consider one of these test, you should know that these tests are primarily used to either "rule in" or "rule out" papillary thyroid cancer, not follicular thyroid cancer. Secondly, you should ask yourself "what information do I seek?" and "How will this information change my approach to my thyroid mass?"
For example, if you have a small thyroid nodule that is less than 1.5 cm (less than a half of an inch) and the FNA is a "follicular neoplasm" and you prefer to monitor the nodule with ultrasound, then all of these tests may lead you to a surgery that you are already not desiring to undergo.
From an opposite standpoint, if you are above 55 years of age and have a 4cm thyroid nodule that has abnormal vascularity and on FNA is a follicular neoplasm as well, then surgical excision would be recommended for multiple reasons including ultrasound appearance, size, and age. Genetic testing could only be beneficial in this circumstance if the surgeon and patient would propose a total thyroidectomy based upon this additional information. What you really need to be able to do is sit down with your expert thyroid cancer surgeon and discuss your particular thyroid mass, personal wishes, and concerns….and arrive upon what is best for you under these circumstances.
The current commercially available genetic testing for thyroid nodules are Veracyte (Afirma), Asuragen, and Thyroseq. These tests have little to no benefit in the diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer. The genetic abnormalities of non-cancers of follicular origin (follicular adenoma and follicular neoplasm of uncertain malignant potential) are also found in follicular thyroid cancers!
- The Veracyte test has the best ability to tell whether the FNA cytology is benign. This is called a “rule out” test.
- Both Asuragen and Thyroseq are “rule in” tests. What this means is that they look for genetic abnormalities known to be associated with a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer. . In particular, the follicular variant of papillary thyroid cancer (see diagnosis of follicular variant of papillary thyroid cancer). Finding these particular genetic changes makes a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer much more likely, and in some circumstances may also play a role in determining the best surgery for the cancer.
If the diagnosis of follicular neoplasm has been rendered, your final diagnosis requires a comprehensive microscopic examination of the thyroid nodule (or mass). In particular, if your doctor has reason to think the nodule is suspicious for a diagnosis of a follicular thyroid cancer based upon the nodule size, symptoms, or ultrasound appearance, the preferred biopsy is either a thyroid lobectomy (removal of the half of the thyroid gland that possesses the nodule) or total thyroidectomy. The selection of which surgery is best is dependent upon the patient factors and wishes, tumor characteristics (size, symptoms), and the thyroid cancer surgeon's expertise. Don't forget, you can't choose your cancer, but you can choose the surgeon that will cure your follicular thyroid cancer. Having the wrong or incomplete surgery is essentially choosing a "bad thyroid cancer". Be thoughtful.
Thyroid lobectomies and total thyroidectomies are done in an operating room while you are under general anesthesia (in a deep sleep).
Total thyroidectomy is generally the preferred treatment for patients with a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer. In the less aggressive variants including follicular neoplasm of uncertain malignant potential and microinvasive follicular thyroid cancer, thyroid lobectomy provides an adequate diagnosis as well as curative surgery. Follicular thyroid cancer exquisitely rarely occurs in more than one site of the thyroid gland! (I have never seen it!)
However, FNA might not be the first test done if you have a suspicious lump in your neck. The doctor might order other tests first, such as blood tests and an ultrasound exam to get a better sense of whether you might have a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer. These tests are described following this section.
Imaging tests for a Diagnosis of Follicular Thyroid Cancer
Imaging tests may be done for a number of reasons, including to help find suspicious areas that might be cancer, to learn how far cancer may have spread, and to help determine the extent of surgery and the role of other treatments or therapies.
People who have or may have a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer will get one or more of the following tests:
Ultrasound
 A high resolution ultrasound machine for evaluation of the thyroid and neck.
A high resolution ultrasound machine for evaluation of the thyroid and neck.
Ultrasound uses sound waves to create pictures inside your neck. The thyroid ultrasound must not only examine the thyroid gland but also must include a comprehensive examination of your neck lymph nodes. For this test, a small, wand-like instrument called a transducer is placed on the skin in front of your thyroid gland and all levels of the neck. It gives off sound waves and picks up the echoes as they bounce off the thyroid (and other underlying neck structures). The echoes are converted by a computer into a black and white image on a computer screen. You are not exposed to any radiation during this test.
This test can help determine if a thyroid nodule is solid or filled with fluid. (Solid nodules are more likely to be cancerous.) It can also be used to check the number and size of thyroid nodules. Further, it can even reveal what the blood supply looks like to these nodules. How a nodule looks on ultrasound can sometimes suggest if it is likely to be a cancer, but ultrasound can’t tell for sure. Importantly, a cystic nodule is most commonly benign (not cancer). However, a cystic lymph node in the bottom half of the neck is most commonly a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer.
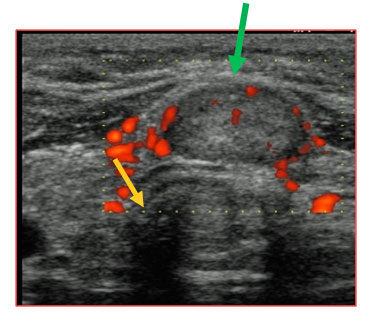 Ultrasound of the thyroid gland. The yellow arrow points to the breathing tube (trachea). The yellow arrow points to a nodule in the middle portion of the thyroid gland. The red colored areas are the abnormal blood flow associated with this thyroid nodule. Fine needle aspiration showed a follicular neoplasm, 1.5 cm in greatest dimenstion. The thyroidectomy revealed this to be an angioinvasive (growing into blood vessels) follicular thyroid cancer.
Ultrasound of the thyroid gland. The yellow arrow points to the breathing tube (trachea). The yellow arrow points to a nodule in the middle portion of the thyroid gland. The red colored areas are the abnormal blood flow associated with this thyroid nodule. Fine needle aspiration showed a follicular neoplasm, 1.5 cm in greatest dimenstion. The thyroidectomy revealed this to be an angioinvasive (growing into blood vessels) follicular thyroid cancer.
For thyroid nodules, ultrasound is used to guide a biopsy needle into the thyroid nodule to obtain a confident sampling of the cells within it.
Expert ultrasound can also help confirm a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer which has spread to the lymph nodes of the neck. The expert ultrasonographer will look for multiple changes. Although many unskilled observers would believe that size is a major issue, but in fact it is not. High resolution ultrasound can detect a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer spread to lymph nodes as small as 1-2 mm (the size of a tip of a ball point pen). When looking at the lymph nodes in the neck with ultrasound, the following are important criteria which may lead to a FNA needle biopsy to confirm disease.
- Full of rounded lymph nodes
- Displacement or disruption of the normal ultrasonic “architecture” of a lymph node
- Cystic lymph nodes
- Microcalcifications within lymph nodes (small ultrasonic calcifications)
- Disorganized vascular flow to the lymph node
- Larger or asymmetric lymph nodes when comparing one side of the neck to the other
- Editorial note: One weakness of ultrasound is that it cannot distinguish cancerous from inflammatory lymph nodes. Both can have very similar appearances however ultrasound guided FNA will provide the necessary microscopic ability to confirm or rule out a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer.
- The quality of the ultrasound machine
- The device that is held in the hand of the technician (the transducer) producing the sound waves
- The experience and the skill of the ultrasound technician
- The experience of the radiologist or diagnostician who is interpreting the study.
We perform an ultrasound on all of our patients ourselves because we have learned that ultrasounds performed elsewhere are not as accurate as we need. The most highly skilled ultrasound will detect abnormalities within lymph nodes within 2 mm. This is approximately the size of a ball point pen head. Your ultrasound should be performed by someone who is specifically dedicated to the ultrasound examination of the thyroid and neck. Experience means everything when you are considering the sensitivity of neck ultrasound.
The ultrasound study will critically look not only at the thyroid but all the tissues in your neck. The ultrasound can show whether something is cystic or solid. It can see the blood supply to a particular area. It can reveal microscopic calcifications that may indicate a cancer. Ultimately, your ultrasound will determine whether a biopsy with a tiny needle is indicated or whether simple blood test may only be indicated. Even if you have already had a biopsy, another biopsy may be indicated if:
- 1. The first biopsy did not provide a diagnosis
- 2. The ultrasound shows something that was previously not seen.
Computed tomography (CT) scan for Follicular Thyroid Cancer
The CT scan of the neck for follicular thyroid cancer is an x-ray test that produces detailed cross-sectional images of your body from the bottom of your brain to the middle of your chest. It can help determine the location and size of thyroid cancer, whether the cancer has invaded into any nearby structures, and whether they have spread to lymph nodes in nearby areas. A CT scan can also be used to look for spread into distant organs such as the lungs.
Generally speaking, a CT scan of the neck is not needed or required for the more common FNA diagnosis of "follicular neoplasm" of the thyroid. However if the follicular neoplasm is clinically suggested to be a high risk lesion for a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer, the a CT scan of the neck is frequently considered.
Potential indications for obtaining a CT scan of the neck for lesions high risk for a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer include:
- Large follicular neoplasm more than 4 centimeters
- Fixed or minimally mobile mass
- Ultrasound suggesting soft tissue extension or invasion
- Patient presenting with symptoms of:
- Vocal cord paralysis
- Difficulty swallowing
A CT scanner has been described as a large donut, with a narrow table in the middle opening. You will need to lie still on the table while the scan is being done. CT scans take longer than regular x-rays, and you might feel a bit confined by the ring while the pictures are being taken.
Instead of taking one picture, like a regular x-ray, a CT scanner takes many pictures while you lie on the table. A computer then combines these pictures into images of slices of the part of your body being studied. A CT scan designed for a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer is sliced at 1mm steps. It is an incredibly detailed study that creates very exquisite images.
Before the test, you will be asked to receive an IV (intravenous) line through which a contrast dye is delivered. This helps better outline structures in your body. The injection may cause some flushing (a feeling of warmth, especially in the face). Some people are allergic and get hives. Rarely, more serious reactions like trouble breathing or low blood pressure can occur. Be sure to tell the doctor if you have any allergies or have ever had a reaction to any contrast material used for x-rays.
You may have heard of a theoretical problem with using CT scans for a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer because the CT contrast dye contains iodine, which interferes with radioiodine scans. This should not be a consideration whatsoever. The iodine for the CT scan will be eliminated from the body in approximately two months. Therefore, at the most, there may just be a slight delay in the timing of radioactive iodine if this is thought to be potentially indicated in the management of the particular diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer. The added information obtained from a CT scan may merely just delay the evaluation of radioactive iodine a month or so.
Insert CT scan of follicular thyroid cancer with soft tissue invasion of esophagus
The CT scan for a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer provides different information to your doctor than the ultrasound. The ultrasound tells the doctor if there is something abnormal. The CT scan tells the doctor where the abnormality is located! Both studies complement each other. The CT scan of the neck also can look at areas of the neck that the ultrasound cannot study because sounds waves cannot pass effectively through bone, cartilage or air. Specifically, the CT scan can effectively see behind the jaw bone (mandible), collar bone (clavicle) or chest wall and also behind the voice box (larynx), breathing tube (trachea), and swallowing tube (esophagus). In all of these sites, the ultrasound examination can be quite limited and therefore a CT scan may provide valuable additional information regarding where the follicular thyroid cancer is and where it is not. Ultimately, all of these studies will determine the extent of required surgery.
In patients with a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer above 45 years of age with advance disease in the thyroid gland itself or spread to lymph nodes, a CT scan of the chest should be obtained. The CT scan of the chest provides an excellent baseline examination (for following) of the lungs and the lymph nodes of the chest, both of these sites the highest risk of distant spread in patients with a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan
Like CT scans, MRI scans can be used to look for a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer in the thyroid, or cancer that has spread to nearby or distant parts of the body. But ultrasound is usually the first choice for looking at the thyroid and neck structures. MRI scans are particularly helpful in looking at the brain and spinal cord.
MRI scans use radio waves and strong magnets instead of x-rays, therefore there is no radiation exposure. The energy from the radio waves is absorbed and then released in a pattern formed by the type of body tissue and by certain diseases. A computer translates the pattern into a very detailed image of parts of the body. A contrast material called gadolinium is often injected into a vein before the scan to better show details.
MRI scans take longer than CT scans – often up to an hour. You may have to lie inside a narrow tube, which can upset people with a fear of enclosed spaces. Newer, more open MRI machines can sometimes be used instead. The machine also makes buzzing and clicking noises, so some centers provide earplugs to block this noise out.
MRI scans are very sensitive to movement and moving during the scanning process produces artifacts that make interpretation difficult. Because people are constantly swallowing and unconsciously moving their voice box and swallowing structures (and therefore their thyroid gland and surrounding lymph nodes, CT of the neck is the preferred cross sectional study of the neck in patients with a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer.
Positron emission tomography (PET)/CT scan
For a PET scan, a radioactive substance (usually a type of sugar related to glucose, known as FDG) is injected into the blood. The amount of radioactivity used is very low. Because cancer cells in the body generally utilize sugar as their energy source to grow, they absorb more of the sugar than normal cells. After waiting about an hour, you lie on a table in the PET scanner for about 30 minutes while a special camera creates a picture of areas of radioactivity in the body.
This test can be very useful if you have a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer that has:
- 1. Come back (recurred) following one or more surgeries
- 2. Diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer that has spread to other sites in the body
- 3. Diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer that doesn’t take up radioactive iodine (called non-iodine avid)
A PET/CT scan may be able to tell whether you have a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer which has spread to other sites of the body.This is almost uniformly observed in patients with a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer that:
- Are above 55 years of age
- Pathology revealed extensive soft tissue invasion (growth into adjacent structures)
- Microscopic examination of the follicular thyroid cells reveal angry looking cells (poorly differentiated or dedifferentiated changes)
- Dedifferentiated or poorly differentiated follicular thyroid cancers (we have a whole section of pathologic subtypes of follicular thyroid cancers)
- A diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer that no longer take up radioactive iodine
- Recurrent Diagnosis of Follicular Thyroid Cancer (Cancers that have “come back” or recurred following one or more previous surgeries)
- A Diagnosis of Follicular Thyroid Cancer which has spread to sites outside of the neck (distant spread)
- A Diagnosis of Follicular Thyroid Cancer where the patient has a blood thyroglobulin level higher than anticipated for the disease that has been found
The PET/CT scan for a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer combines images of both a PET and CT scan at the same time. PET images alone are not very detailed. The computer shows the relative amount of radioactivity to a particular area and where the sugar is localized and it appears red or “hot”. The combination of these two images lets the doctor compare an abnormal area on the PET scan with its detailed appearance and location on the CT scan.
Insert PET/CT scan of diffusely metastatic thyroid cancer
PET/CT scanning is not always positive in patients with a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer.
Indications for obtaining a PET/CT scan for patient with a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer includes:
Blood Tests
Blood tests alone cannot tell the extent of a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer. Blood tests are a tool used with other studies, to monitor the adequacy of your thyroid hormone levels produced by your thyroid or by the intake of prescription thyroid hormones.
Thyroid cells and follicular thyroid cancers can also produce a protein called thyroglobulin which can be used as a blood monitoring tool in some patients.
(Importantly, some patients have an inflammatory condition of their thyroid called thyroiditis. The cause of this inflammation is called an autoimmune disease. This is the body reacting against itself. Some patients with autoimmune thyroiditis will produce an antibody to thyroglobulin. In those circumstances, analysis of thyroglobulin in monitoring a patient with a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer is quite limited since the antibody interferes with the blood analysis of thyroglobulin in these patients.)
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
Tests of blood levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH or thyrotropin) may be used to check the overall activity of your thyroid gland or how much thyroid hormone pill your body requires. Levels of TSH, which is made by a gland in the brain called the pituitary gland, may be high if you do not have enough thyroid hormone in your body. In previously untreated patients with a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer, their TSH level is usually normal. In patients with a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer that are being prepared for radioactive iodine treatment, they are most commonly taken off of thyroid hormone and their doctor will measure their TSH level which should be markedly elevated (radioiodine scans require the body to be hypothyroid). Alternatively, a medicine called Thyrogen (which is TSH produced as a drug) can also be given to patients with a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer by injection to make the body “appear” to be hypothyroid. After patients with a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer have undergone their surgery, their endocrinologist will likely want to keep their TSH level low to prevent stimulation of your thyroid gland and the potential stimulation of undetectable microscopic follicular thyroid cancer cells.
T3 and T4 (thyroid hormones)
These are the main hormones made by the thyroid gland. Levels of these hormones may also be measured to get a sense of overall thyroid gland function. The T3 and T4 levels are usually normal in patients with a previously untreated diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer. Follicular thyroid cancer rarely produces rarely produces either T3 or T4 hormones. Interesting, even in patients with a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancers that are quite massive with very little normal appearing thyroid tissue, hypothyroidism is quite infrequent as well.
Thyroglobulin
Thyroglobulin is a protein made by the thyroid gland that can be measured in blood sampling. Measuring the thyroglobulin level in the blood can’t be used to make a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer, but it can be helpful after treatment to determine whether the patient has (or does not) have disease. A common way to treat patients with a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer is to remove most or all of the thyroid gland by surgery and then use radioactive iodine to destroy any remaining thyroid cells. In patients with a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer, which have undergone total thyroidectomy with or without radioactive iodine treatment, their blood marker for thyroglobulin should be very low within several weeks of their surgery.
- There is still follicular thyroid cancer cells in the body
- There remains more thyroid tissue in the body which is producing thyroglobulin that has not been removed.
- There remains more thyroid tissue in the body which has not been destroyed by radioactive iodine treatment.
Importantly, in patients with a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer who have undergone total thyroidectomy, if the thyroglobulin level rises again after being low, it is a sign that the cancer has almost certainly recurred.
Thyroglobulin Antibodies
Some patients have an inflammatory condition of their thyroid gland called thyroiditis. The most common cause of thyroiditis is a condition where the body produces an immune reaction to normal thyroid tissue. The body’s immune reaction is the production of an antibody and in autoimmune thyroiditis this can result in an antibody to the protein normally produced by thyroid cells called thyroglobulin. These thyroglobulin antibodies directly bind (grab onto thyroglobulin).
Very importantly, in patients with a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer who also have thyroiditis, their antibodies to thyroglobulin directly bind to thyroglobulin, and make the blood level of thyroglobulin appear to be zero (because the antibodies are clumped with the thyroglobulin protein and then not detected in the blood test).
Whenever the marker thyroglobulin is checked in the blood, the antibody to thyroglobulin must also be measured. If the antibody to thyroglobulin is detected, measuring thyroglobulin in the blood is not an effective marker in patients with a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer.
Other Blood Tests
You might have other blood tests as well. For example, if you are scheduled for follicular thyroid surgery, tests will be done to check your blood cell counts, to look for bleeding disorders, and to check the function of your liver and kidneys.
Other Tests
Vocal cord exam (laryngoscopy)
Thyroid tumors can sometimes affect the function of your voice box. Even if your voice sounds normal to you and others, this does not mean that your vocal cords are functioning normally. If you are going to undergo a surgery for a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer, a procedure called a laryngoscopy will probably be done first to see if the vocal cords are moving normally. For this exam, the doctor looks through the nose or down the throat at the larynx (voice box) with a special thin tube with a light and a lens on the end for looking at the voice box. This special tiny scope is inserted through the nose and there is little to no discomfort associated with the examination. Alternatively, sometimes a mirror can be used to see the voice box as well.
For the Diagnosis of Follicular Thyroid Cancer: The Best Treatment is a Good Surgery!
The diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer (carcinoma) is best treated almost exclusively by a good surgery. A good surgery is performed by a highly experienced surgeon. The best surgery provides a patient with a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer the best opportunity for long term control and cure of their cancer. In contrast, an incomplete surgery may greatly increase the risk of:
- recurrence
- invasion of the follicular thyroid cancer into important structures in the neck
- ultimately the ability to be cured of the follicular thyroid cancer.
The optimal extent of initial surgery is determined by the ultrasound of the thyroid and neck to look closely at the thyroid gland and the lymph nodes of the neck. The section of ultrasound in the diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer has a great general overview of the importance of high resolution ultrasound in the evaluation of follicular thyroid cancer. If there are any abnormal lymph nodes of the neck that have worrisome characteristics the next step is almost always a needle biopsy. If there is any suspicion of extensive of the follicular thyroid cancer into adjacent structures, a CT scan of the neck with contrast is the preferred x-ray and should be obtained.
Quick Facts!!!
- The risk of the diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer is directly related to the size of the follicular neoplasm within the gland itself.
- The diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancers that are less than 1.5 cm in size (less than ½ inch) have the best cure rates (nearly 100% for small follicular thyroid cancers in young patients). For this reason, the diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer is sometimes referred to as “the good cancer”.
- The diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer that develops in men that are above 55 years of age may be more difficult cancers to control in contrast to younger women.
- The diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer is rarely associated with spread to lymph nodes of the neck.
- The diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer is rarely associated with high thyroid function (hyperthyroidism) or low thyroid function (hypothyroidism).
- The diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer, in patients above 60 years of age, has a significant risk of lung metastasis when vascular invasion and soft tissue invasion is found grossly (with xray and clinical findings).
The Diagnosis of Follicular Thyroid Cancer is Not Commonly Associated with Spread to Distant Areas Outside of the Neck (distant sites= distant metastases=spread to other parts of the body)
- The diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer spread to distant sites of the body is uncommon.
- When it does spread to other areas of the body, the lungs and then bones are the most commonly found involved locations followed by the liver.
- The diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer spread to distant sites is serious and requires an interdisciplinary thyroid cancer team that is very knowledgeable about the patient and the cancer itself.
- Distant spread of follicular thyroid cancer can make these cancers to behave quite similar to other cancers that we all fear.
- The diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer spread to distant sites significantly increases the risk of dying from this thyroid cancer.
- Importantly, despite the diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer spread to distant sites, expert surgery remains a critical part of treatment in effectively controlling where the cancer began in the thyroid as well as spread to the neck lymph nodes.
- The diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer with distant spread in the body is an indication for radioactive iodine treatment.
- Total thyroidectomy should be performed for the diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer with distant spread.
- The diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer involving distant sites in the body is frequently associated with cancers that:
- have been diagnosed in older patients above 55 years of age
- exhibited significant vascular invasion within the thyroid gland or neck blood vessels
- are larger (the larger the follicular thyroid cancer the greater the risk of distant metastases)
- have shown growth into surrounding structures around the thyroid gland (such as growth into the muscles of the neck, trachea (breathing tube), esophagus (swallowing tube).
Diagnosis of Follicular Thyroid Cancers-Pathologic Types
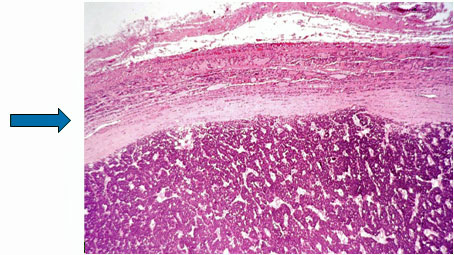 The blue arrow points to the markedly thickened capsule of the follicular thyroid cancer. There is no visualized cancer invasion of blood vessels or the capsule of the cancer.
The blue arrow points to the markedly thickened capsule of the follicular thyroid cancer. There is no visualized cancer invasion of blood vessels or the capsule of the cancer.
- Well Differentiated Follicular thyroid cancer-with uncertain malignant potential
- Good surgery is the mainstay of treatment
- Exquisitely low risk of spread to lymph nodes
- Cannot be diagnosed with FNA
- Not a radiation induced cancer
- Multicentricity of the thyroid does not occur (Other similar areas within the thyroid gland are not observed)
- The genetic defects associated with the diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer are also observed in the benign follicular lesions!!
- Total Thyroidectomy is the mainstay of treatment
- Radioactive iodine treatment is commony prescribed
- Lymph node metastases are very rare
- Not able to be diagnosed with fine needle aspiration (FNA)
- Surgery is required to determine the diagnosis of angioinvasive follicular thyroid cancer
- Long term outcomes based upon age of the patient and degree of vascular invasion (older patients with more vascular invasion have a greater risk of spread to distant sites and mortality)
- Genetic alterations do not distinguish this from benign follicular lesions.
- Widely Invasive Follicular Thyroid Cancer (with Extensive Soft Tissue Invasion)
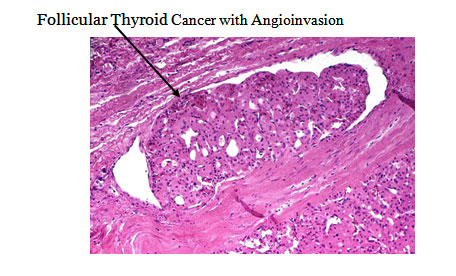 The black arrow points to follicular thyroid cancer cells within a blood vessel. This is required to make a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer with angioinvasion.
The black arrow points to follicular thyroid cancer cells within a blood vessel. This is required to make a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer with angioinvasion.
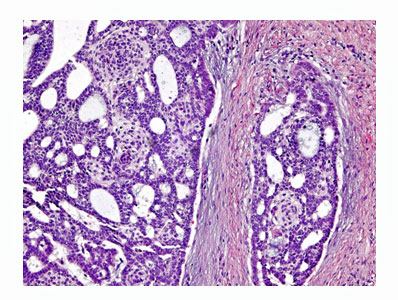 The darkish blue/purple cells are a widely invasive follicular thyroid cancer. The cancer in this picture is invading the capsule of the gland. This was found in multiple other sites of the thyroid as well as into blood vessels. This is a diagnosis of a follicular thyroid cancer that has the potential to spread to distant sites of the body.
The darkish blue/purple cells are a widely invasive follicular thyroid cancer. The cancer in this picture is invading the capsule of the gland. This was found in multiple other sites of the thyroid as well as into blood vessels. This is a diagnosis of a follicular thyroid cancer that has the potential to spread to distant sites of the body.
The diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer may also be associated with the following:
- A long standing history of a lump in the thyroid gland
- A long standing history of thyroid goiter
- " A low iodine diet
- Editorial note: The diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer is not commonly associated with any risk factors. (For more information see section on Follicular Thyroid Cancer Genetics and Special Cases)